As environmental awareness deepens and climate concerns intensify, people are moving beyond sustainability toward a more holistic approach known as regenerative living. Unlike traditional environmental strategies that focus on reducing harm, regenerative approaches aim to restore and enhance ecosystems, communities, and resources. This shift is reshaping how individuals design homes, consume goods, grow food, and interact with nature. A sustainable lifestyle remains essential, but regenerative thinking expands it by emphasizing positive ecological impact. Through intentional eco practices, households and communities can actively contribute to environmental renewal rather than merely minimizing damage.
The rise of regenerative living reflects a broader transformation in environmental philosophy. Sustainability often focuses on maintaining balance, while regenerative systems seek improvement and restoration. By adopting regenerative principles, individuals integrate eco practices such as soil restoration, circular consumption, and renewable resource use into daily routines. This evolution of sustainable lifestyle thinking encourages long-term ecological resilience rather than short-term conservation. By 2026, regenerative living is emerging as a guiding framework for environmentally conscious living across urban and rural environments.
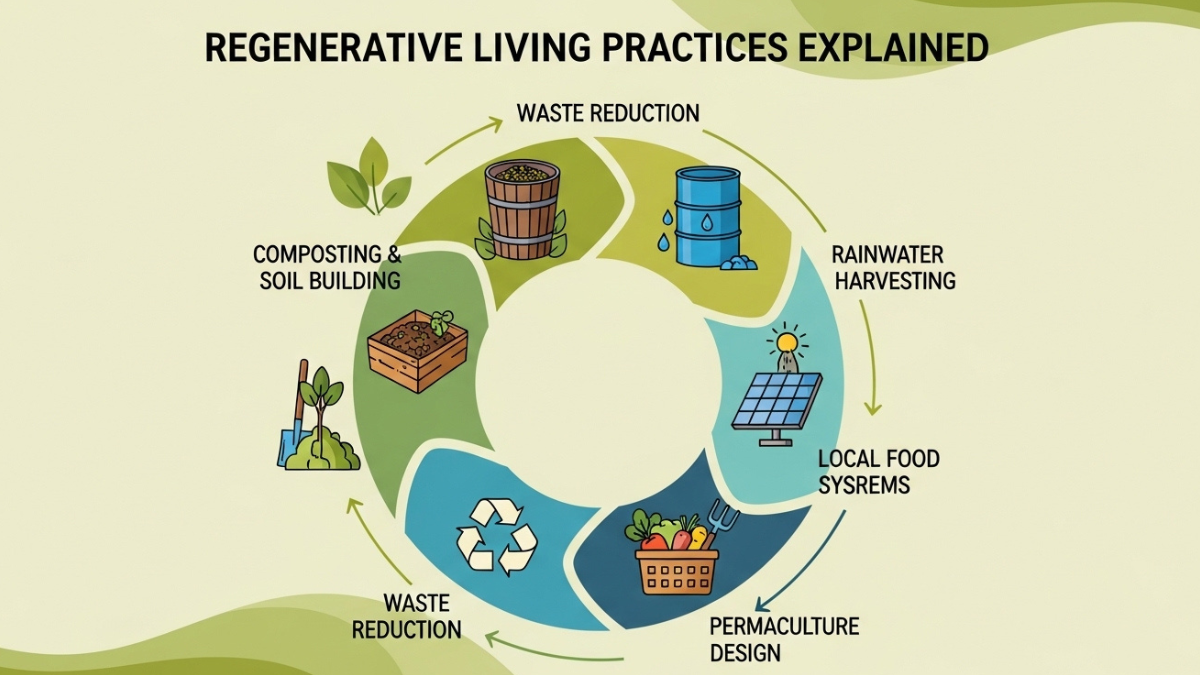
Core Principles of Regenerative Living
At its foundation, regenerative living is guided by principles that emphasize restoration, circularity, and interdependence with natural systems. These principles extend beyond environmental actions to include social and economic dimensions. A sustainable lifestyle aligned with regenerative values supports biodiversity, resource regeneration, and community well-being. Implementing consistent eco practices enables individuals to contribute to ecological restoration in everyday life.
Key principles of regenerative living include:
- Restoring ecosystems and soil health
- Using renewable and regenerative resources
- Minimizing waste through circular systems
- Supporting local and ethical production
- Enhancing biodiversity and natural cycles
These principles illustrate how eco practices shift from minimizing impact to creating positive environmental outcomes. By integrating regenerative approaches into a sustainable lifestyle, individuals and communities can actively repair ecological systems. The philosophy of regenerative living promotes long-term environmental health rather than temporary conservation measures.
Regenerative Living in Food and Agriculture
Food production and consumption are central to regenerative living, as agriculture directly affects soil, biodiversity, and climate. Regenerative agriculture focuses on restoring soil fertility, increasing carbon sequestration, and promoting biodiversity. Consumers adopting eco practices such as local sourcing, organic food choices, and seasonal eating support regenerative food systems. A sustainable lifestyle aligned with regenerative principles prioritizes nutrient-dense food grown through environmentally restorative methods.
Examples of regenerative food practices include:
- Supporting regenerative and organic farms
- Growing home or community gardens
- Composting food waste
- Choosing seasonal and local produce
- Reducing industrially processed foods
These actions demonstrate how eco practices connect consumption with ecological regeneration. By aligning dietary habits with regenerative living, individuals support soil health and biodiversity. Integrating regenerative food choices into a sustainable lifestyle contributes to healthier ecosystems and communities.
Regenerative Living in Homes and Daily Consumption
Homes and consumption patterns also play a major role in regenerative living. Beyond energy efficiency, regenerative households aim to produce resources and restore environmental quality. Implementing eco practices such as renewable energy, water conservation, and natural materials supports ecological balance. A sustainable lifestyle becomes regenerative when homes contribute positively to ecosystems.
Key regenerative home practices include:
- Installing solar or renewable energy systems
- Harvesting rainwater and conserving water
- Using natural and non-toxic materials
- Creating biodiversity-friendly gardens
- Reducing and recycling waste
These eco practices transform homes into regenerative environments rather than passive consumers of resources. By integrating such approaches into regenerative living, households enhance ecological resilience. The evolution of sustainable lifestyle design is shifting toward regenerative architecture and resource-positive homes.
Below is a comparison of sustainable and regenerative living approaches:
| Aspect | Sustainable Lifestyle | Regenerative Living |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Reduce harm | Restore and improve |
| Resource use | Efficient | Renewable and regenerative |
| Waste approach | Minimize | Circular systems |
| Food choices | Organic, local | Soil-restoring agriculture |
| Energy | Renewable use | Energy-positive homes |
| Environmental impact | Neutral | Positive |
This comparison highlights how regenerative living extends beyond traditional sustainability. While a sustainable lifestyle focuses on conservation, regenerative approaches aim for ecological renewal through proactive eco practices.
Community and Social Dimensions of Regenerative Living
The philosophy of regenerative living extends beyond individual behavior to community systems and social structures. Regenerative communities emphasize collaboration, local economies, and shared environmental responsibility. Collective eco practices such as community gardens, cooperative energy systems, and local production networks strengthen resilience. A sustainable lifestyle becomes more impactful when supported by community participation.
Community-based regenerative actions include:
- Local food cooperatives and markets
- Community renewable energy projects
- Shared green spaces and reforestation
- Circular economy initiatives
- Environmental education programs
These initiatives demonstrate how eco practices scale from individual to collective impact. By embedding regenerative principles into communities, regenerative living fosters ecological and social well-being. Integrating regenerative approaches into a sustainable lifestyle enhances both environmental and community resilience.
Future Trends in Regenerative Living
The future of regenerative living is closely linked to innovation in ecological design, circular economies, and environmental restoration technologies. Urban planning is increasingly integrating green infrastructure and regenerative architecture. Technology-enabled eco practices such as smart water systems and regenerative materials are shaping sustainable cities. As awareness grows, sustainable lifestyle frameworks are evolving into regenerative living ecosystems.
Emerging trends shaping regenerative living include:
- Regenerative urban design and green cities
- Circular product and packaging systems
- Bio-based and regenerative materials
- Nature-integrated architecture
- Technology-supported ecological restoration
These developments will transform eco practices into mainstream lifestyle standards. By integrating ecological restoration into everyday systems, regenerative living will redefine sustainability for future generations. The transition from a sustainable lifestyle to regenerative living represents a significant evolution in environmental consciousness.
Conclusion
By 2026, regenerative living is emerging as a transformative approach to environmental responsibility and lifestyle design. Moving beyond conservation, it emphasizes restoration, renewal, and positive ecological impact. Through consistent eco practices and intentional choices, individuals and communities can actively regenerate natural systems. Integrating regenerative principles into a sustainable lifestyle supports biodiversity, resource renewal, and long-term environmental resilience. As global awareness and innovation expand, regenerative living is poised to become the foundation of future sustainable societies and ecological well-being.
FAQ
What is regenerative living?
Regenerative living is a lifestyle approach focused on restoring ecosystems and creating positive environmental impact rather than just reducing harm.
How is regenerative living different from sustainable lifestyle?
A sustainable lifestyle aims to minimize environmental damage, while regenerative living actively improves and restores ecological systems.
What are examples of eco practices in regenerative living?
Eco practices include composting, regenerative agriculture, renewable energy use, and biodiversity-friendly home design.
Can regenerative living be practiced in cities?
Yes, urban regenerative living includes green architecture, community gardens, and circular resource systems.
Why is regenerative living important?
Regenerative living helps restore ecosystems, improve biodiversity, and support long-term environmental health.
Click here to know more.